VBA: Introduction to VBA macros and Its Uses for beginners
- Fakhriddinbek

- Sep 28, 2025
- 5 min read
When you think about Microsoft Office applications like Excel, Word, or PowerPoint, you may imagine spreadsheets, documents, and slides. But did you know that behind these tools lies a powerful automation engine called VBA (Visual Basic for Applications)? Whether you are a student, analyst, business professional, or even a curious learner, understanding VBA can transform the way you work.
In this article, we’ll dive into what VBA is, why it’s important, and how you can start using it right away—even if you’ve never written a line of code before. By the end, you’ll see how VBA can save you hours of manual work, boost your productivity, and open new opportunities in the digital workplace.
What is VBA macros?
VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) is a programming language developed by Microsoft. It is built into most Office applications like Excel, Word, PowerPoint, Access, and Outlook.
Think of VBA as your personal assistant inside Office. Instead of repeating the same clicks and actions, VBA allows you to automate tasks, build custom tools, and even create user-friendly interfaces.
For example:
In Excel, you can use VBA to clean thousands of rows of data in seconds.
In Word, you can create macros to format long documents instantly.
In Outlook, VBA can automatically sort and respond to emails.
Why Should You Learn VBA?
If you’re wondering whether learning VBA is worth your time, here are some strong reasons:
Saves Time: Automating repetitive tasks saves hours of manual effort.
Improves Accuracy: Reduces human error in data entry or formatting.
Boosts Career Opportunities: Employers value employees who can automate and optimize workflows.
Customizes Office Applications: Tailor Excel, Word, or PowerPoint to your exact needs.
Cost-Effective: Unlike other automation tools, VBA comes free with Microsoft Office.
Where is VBA Used?
VBA is used in multiple industries and professions. Here are a few practical examples:
Finance and Accounting: Automating reports, reconciling accounts, and building dashboards.
Data Analysis: Cleaning, transforming, and analyzing large datasets in Excel.
Project Management: Automating schedules and creating progress reports.
Administration: Generating Word letters, PowerPoint presentations, or sending bulk emails from Outlook.
Education: Building interactive learning tools and simplifying grading systems.
Step-by-Step Guide: Getting Started with VBA
Now that you know what VBA is and why it matters, let’s walk step by step through how to start using it.
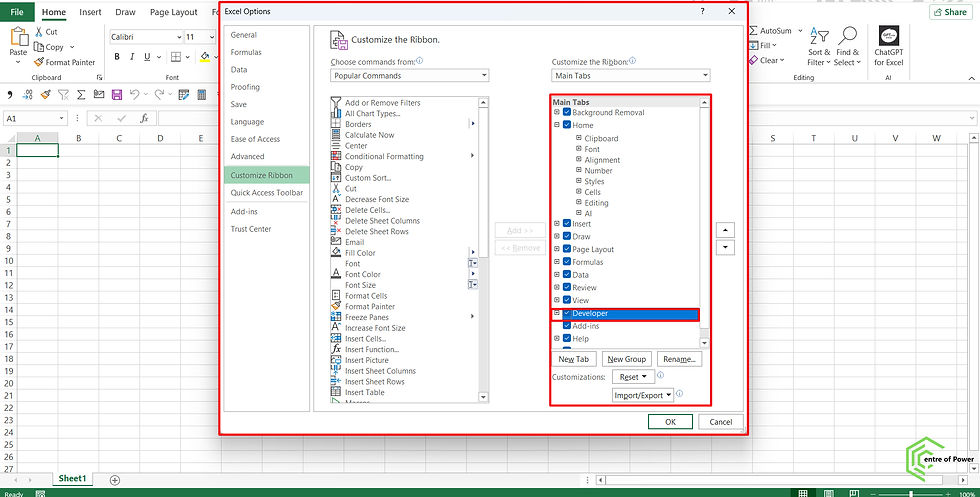
Step 1: Enable the Developer Tab in Office
By default, VBA tools are hidden. To access them:
Open Excel (or Word/PowerPoint).
Click on File > Options > Customize Ribbon.
Check the box for Developer.
Click OK.
You’ll now see the Developer Tab on the ribbon.

Step 2: Open the VBA Editor
Go to the Developer Tab.
Click on Visual Basic.
Alternatively, press Alt + F11 on your keyboard.
A new window called the VBA Editor will appear. This is where you write and manage your code.

Step 3: Record Your First Macro
Macros are the easiest way to start with VBA because they record your actions and convert them into code.
In Excel, go to the Developer Tab and click Record Macro.
Give your macro a name (e.g., Formatting_cells).
Perform a few actions—like formatting cells, applying bold, or adding borders.
Stop recording.
Now, when you run the macro, Excel will repeat the same steps automatically.
Step 4: View the VBA Code Behind Your Macro
Open the VBA Editor (Alt + F11).
On the left panel, you’ll see a folder named Modules.
Open the module, and you’ll find the VBA code generated by your recorded macro.
This is your first step toward understanding how VBA works!
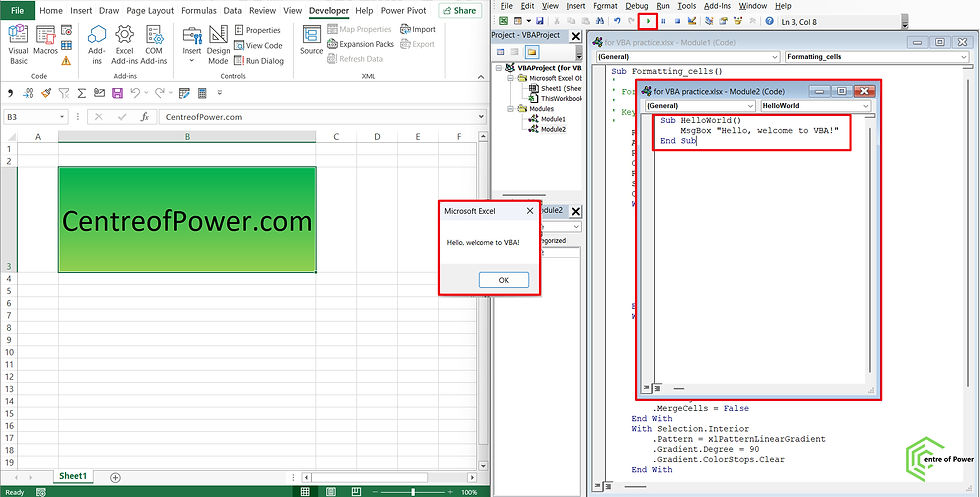
Step 5: Write a Simple VBA Code
Let’s write a small code to display a message box.
Sub HelloWorld()
MsgBox "Hello, welcome to VBA!"
End Sub
How to run it:
Go to the VBA Editor.
Insert > Module.
Copy and paste the above code.
Press F5 to run it.
You’ll see a pop-up message saying Hello, welcome to VBA!

Step 6: Automate a Real Task in Excel
Here’s a practical example: clearing data from a specific range in Excel.
Sub ClearData()
Range("A2:D100").ClearContents
End Sub
Whenever you run this code, it will instantly clear the data from cells A2 to D100—much faster than doing it manually.
Step 7: Explore Advanced Features
Once you’re comfortable with the basics, VBA can help you achieve more:
Loops: Repeat actions automatically.
Conditions (If…Then): Run actions based on rules.
User Forms: Create input forms for better user interaction.
Integration: Connect Excel with Word, Outlook, or even databases.

To save the file it should have Macro enabled format.
Here is the practice file that was used for this post. You can copy the code and see its action when you press "run".
Best Practices for Learning VBA
Start Small: Begin with simple tasks like formatting or creating message boxes.
Practice Regularly: Use VBA in your daily work, no matter how small the automation is.
Use the Macro Recorder: Record actions, then study the code to learn.
Debug Your Code: Use breakpoints and the Immediate Window to test.
Read and Experiment: Search for sample codes online and modify them to fit your needs.
Benefits of Using VBA in Real Life
In Excel: Automate data cleaning, reporting, chart creation, and financial models.
In Word: Generate contracts, format legal documents, or create templates.
In PowerPoint: Automate slide creation for meetings or client presentations.
In Outlook: Schedule emails, organize folders, and respond to clients faster.
Common Challenges Beginners Face
Fear of Coding: Many think coding is hard—but VBA is beginner-friendly.
Errors and Bugs: Mistakes happen; learning how to debug is part of the process.
Not Knowing Where to Start: Begin with small macros and build gradually.
VBA is not just for programmers—it’s for anyone who wants to work smarter, not harder. By investing a little time in learning VBA, you can save hours every week, reduce stress, and impress your boss or clients with powerful automation.
Start today! Open Excel, record a macro, and peek into the VBA Editor.
Set yourself a small automation challenge—like formatting a sheet or sending an email.
Keep learning step by step, and soon, you’ll be building tools that make your work life easier.
Remember, VBA is a hidden gem inside Microsoft Office. Once you unlock its power, you’ll wonder how you ever worked without it.



Comments